Elevating excellence isn’t just a goal in product design; it is essential for staying competitive and meeting user expectations. This week, we explore strategies to scale and strengthen design teams for optimal performance. Through assessing current practices, building a strong foundation, strategic hiring, and commitment to scaling, organizations can enhance their product design teams effectively. This guide outlines actionable steps and strategies to navigate this journey toward product design excellence.
Understanding UX Maturity
UX maturity measures an organization’s ability and commitment to delivering user-centered design. It encompasses the quality and consistency of research and design processes, resources, tools, and operations, as well as the organization’s support and commitment to UX through leadership, workforce, and culture. Assessing UX maturity helps organizations understand their current strengths and weaknesses and provides a roadmap for improvement.
According to Forbes, studies show that companies that invest in UX see a lower cost of customer acquisition, lower support cost, increased customer retention, and increased market share.
Forrester has found that every $1 invested in UX results in a return of $100, a 9,900% ROI.
The UX Maturity Model
The UX Maturity Model offers a framework to evaluate an organization’s UX capabilities across six stages:
- Absent: UX is ignored or nonexistent.
- Limited: UX work is rare, haphazard, and lacks importance.
- Emergent: UX efforts are functional but inconsistent and inefficient.
- Structured: UX processes are semi-systematic and widespread but vary in effectiveness.
- Integrated: Comprehensive and effective UX work is pervasive across the organization.
- User-Driven: Dedication to UX at all levels results in deep insights and exceptional user-centered outcomes.
Factors in UX Maturity
None of these factors stand alone. They reinforce and enable each other. A holistic approach is essential to advance UX maturity and realize the full value of user-centered design.
- Strategy: UX leadership, planning, and resource prioritization.
- Culture: Cultivating UX knowledge and career growth for practitioners.
- Process: Systematic use of UX research and design methods.
- Outcomes: Defining and measuring UX results.
Assessing Current Processes and Practices
In assessing your current design processes and practices, it is crucial to identify both strengths and areas for improvement within your workflow. This evaluation provides insight into what is functioning well and where challenges exist.
Assessment of Current Practices
- What aspects of our current design practice work well, and why?
- Where do we encounter bottlenecks or inefficiencies?
Tools and Technologies
- Are the tools and technologies we use meeting our needs?
- Are there new tools or technologies we should consider adopting?
- Design Standards and Guidelines
- Do we have a comprehensive set of design standards and guidelines?
- How well are these guidelines communicated and adhered to?
A thorough evaluation highlights strengths and uncovers areas that need improvement. Addressing these aspects helps streamline workflows, adopt better tools, and ensure adherence to standards, ultimately enhancing overall design quality and consistency.
Building a Strong Foundation
Establishing a solid foundation is crucial for scaling and strengthening a product design team. This involves ensuring that the basics are robust and well-defined.
Key Components of a Strong Foundation
- Clear Design Vision
- Design Systems
- Tools and Resources
These components empower efficient scaling and strengthening of product design teams.
Clear Design Vision and Strategy
A clear design vision and strategy align the team’s efforts with company goals. This means defining a long-term vision that inspires and guides the team.
- Vision Statement: Develop a statement that encapsulates the desired user experience, such as creating intuitive, accessible, and delightful digital experiences.
- Strategic Goals: Set goals that support the vision, including improving satisfaction scores or increasing engagement metrics.
With a clear vision and strategy, teams can prioritize work and make decisions that support broader business objectives.
Design Systems
Implementing a design system ensures consistency and efficiency across design efforts. A design system includes reusable components, guidelines, and standards that maintain a coherent visual and interaction language.
- Component Library: A shared library of UI components such as buttons, forms, and navigation elements.
- Style Guide: A comprehensive guide covering typography, color palettes, iconography, and visual elements.
A well-maintained design system streamlines the design process, reduces redundancy, and keeps team members aligned.
Tools and Resources
Ensuring access to modern design tools and resources is critical for efficiency and innovation.
- Design Software: Industry-standard tools like Figma for collaboration and prototyping.
- User Research Tools: Platforms like UserTesting, Marvin, and Hotjar for usability testing and behavioral insights.
- Collaboration Platforms: Tools such as Slack, Trello, or Asana for communication and project management.
Equipping teams with the right tools empowers them to produce higher-quality work more effectively.
Hiring and Team Structure
To effectively scale a product design team, a strategic approach to hiring and structure is essential. This includes assessing skills, fostering professional development, ensuring diversity, organizing teams efficiently, and establishing strong leadership.
In one referenced video, Joel Califa, former Product Designer at GitHub, shares lessons on structuring teams to meet business and organizational needs, determining who to hire, and setting hires up for success.
Skills Assessment
A thorough skills assessment identifies strengths and weaknesses within the team.
- Inventory of Skills: Map existing capabilities such as UX research, UI design, prototyping, and accessibility.
- Gap Analysis: Identify areas lacking expertise and address them through hiring or training.
Professional Development
Continuous learning keeps teams updated with trends and best practices.
- Training Programs: Access to courses and certifications from platforms like Coursera or Nielsen Norman Group.
- Conferences and Events: Attendance at UXPA, IxDA, or SmashingConf.
- Internal Knowledge Sharing: Regular sessions for presenting learnings or case studies.
Diverse Talent
Hiring varied skill sets ensures comprehensive design coverage.
- UX Researchers focus on behavior and needs.
- UI Designers specialize in visual interfaces.
- Interaction Designers shape user flows.
- Content Designers craft user-centered messaging.
- Design System Managers oversee system consistency.
- Graphic Designers enhance aesthetics and brand expression.
Team Structure
- Cross-Functional Squads or Pods: Small teams combining designers, developers, and product managers focused on specific areas.
- Centralized vs. Decentralized Teams: Centralization offers consistency and shared resources, while decentralization increases agility and responsiveness.
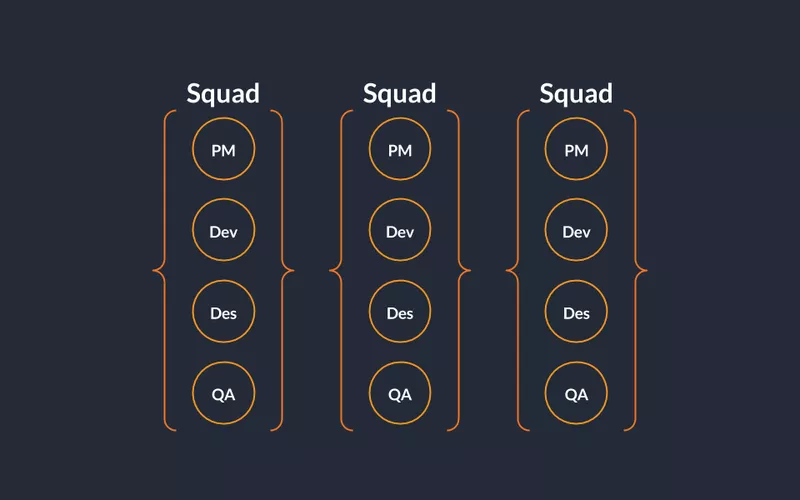
Caption: Buffer, a social media management platform, organizes its teams into squads.
Leadership
Strong leadership advocates for design value at the highest level. Appointing roles such as Chief Creative Officer, Chief Experience Officer, or VP of Design ensures design has executive representation.
- Advocacy: Champions design in strategic discussions.
- Mentorship and Growth: Supports junior designers and attracts top talent.
Scaling and Future Growth
As organizations expand, scaling design practices becomes increasingly important. This involves addressing growth challenges, implementing scalable processes, and strengthening knowledge sharing and documentation.
Case Study: Airbnb
Airbnb structures its design organization to promote scalability while maintaining creativity and collaboration.
- Cross-Functional Teams integrate designers with engineers and product managers.
- DesignOps supports workflows, systems, and resources.
- Design System DLS maintains consistency and collaboration.
- Distributed Teams tap global talent pools.
- Culture of Feedback and Learning encourages open critiques and growth.
Scaling Practices
- Maintaining Consistency through robust design systems.
- Coordination Across Teams with cross-functional squads and shared documentation.
- Scaling Research Efforts with centralized repositories and tools like Dovetail.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention through strong employer branding and growth opportunities.
Knowledge Sharing and Documentation
- Effective documentation ensures continuity and improvement.
- Process Documentation with step-by-step guides.
- Decision Logs capturing rationale.
- Outcome Reporting through retrospectives and metrics.
- Regular Knowledge-Sharing Sessions and Collaborative Platforms.
- Mentorship Programs to transfer skills and build culture.
A Practical Plan for Scaling
Phase 1 Foundation
- Assess maturity
- Establish vision and strategy
- Appoint design leadership
- Implement a design system
Phase 2 Growth
- Hire diverse talent
- Invest in tools and learning
- Integrate design thinking
Phase 3 Optimization
- Refine processes
- Measure impact
- Foster continuous improvement
Championing Quality from the Top Down and Bottom Up
Top-Down Approach
- Executive Support through direct reporting lines.
- Design Thinking Culture involving leadership participation.
- Investment in Design through budgets and resources.
Bottom-Up Approach
- Continuous Learning through education and events.
- Feedback Mechanisms with critiques and reviews.
- Empowerment giving designers autonomy and ownership.
Case Study: IBM
Top-Down Leadership: IBM established a Chief Design Officer role reporting directly to the CEO, embedding design into strategy.
Bottom-Up Empowerment: Company-wide design thinking workshops and internal communities encourage collaboration and growth.
Handling Lack of Prioritization
- Educate Stakeholders with case studies and data.
- Deliver Quick Wins to demonstrate value.
- Internal Advocacy from design leaders in meetings and strategy sessions.
- Establish Metrics to Measure the Impact and Quality of Design
- Metrics provide tangible data to guide decisions and demonstrate value.
Trackable Metrics
- Surveys including NPS
- Usability Testing measuring success rates and errors
- Design Efficiency
- Time Tracking across phases
- Iteration Cycles monitoring refinements
- Business Iimpact
- Conversion rates through A/B testing
- User retention via cohort analysis
- Revenue impact through sales and lifetime value metrics
Collaboration and Communication
Assess collaboration effectiveness between designers, developers, and stakeholders.
- Use tools like Figma or Miro for real-time feedback.
- Establish structured communication channels and visual aids.
- Provide training in communication skills.
Feedback and Reflection
- Assess feedback mechanisms such as usability tests and stakeholder reviews.
- Streamline feedback loops with scheduled sessions and tools.
- Reflect on past projects to document lessons learned and integrate improvements into future work.
Actionable Steps
Set Goals
- Define clear objectives such as improving consistency or increasing satisfaction.
Establish metrics to track progress
- Implementation Plan
- Identify quick wins like adopting tools or improving documentation.
- Assign responsibility and timelines with regular reviews.
Parting Words
Scaling and strengthening a product design team requires strategic leadership, clear processes, continuous learning, and a strong culture of design thinking. By following a structured plan and championing quality from both the top down and bottom up, organizations can build better products and foster lasting innovation.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding UX Maturity is essential for identifying strengths and creating improvement roadmaps.
- Building a Strong Foundation through vision, systems, and resources enables scale.
- Hiring and Team Structure drive effectiveness and adaptability.
- Scaling and Future Growth require coordination, documentation, and knowledge sharing.
- Championing Quality at all organizational levels ensures sustained design excellence.
- Pernice, K., Gibbons, S., Moran, K., & Whitenton, K. The 6 Levels of UX Maturity. Nielsen Norman Group.

Leave a Reply